RAPID BRIDGE REPLACEMENT PROJECT
STATEWIDE, PA
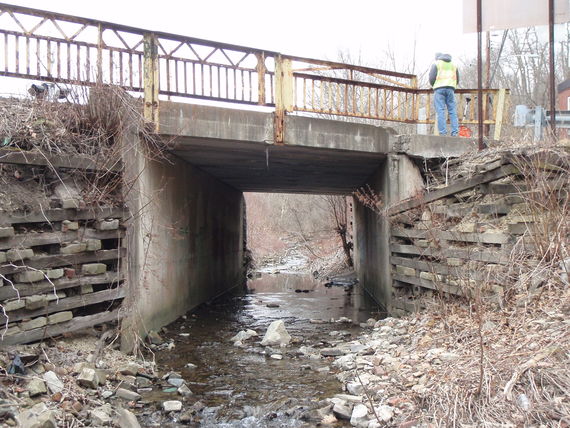
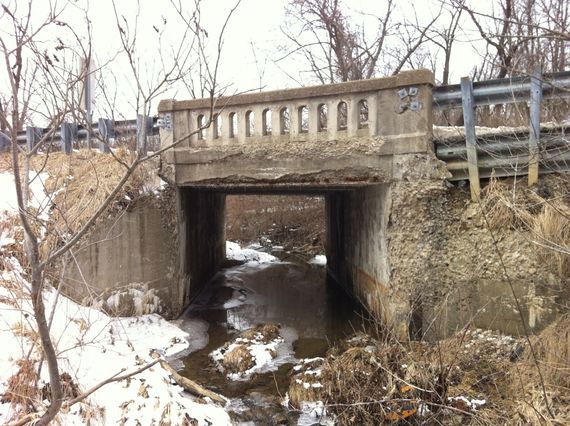
The Rapid Bridge Replacement project is comprised of 558 bridges across Pennsylvania that are being replaced on an accelerated schedule through public-private partnership.
THE CHALLENGE
The Rapid Bridge Replacement (RBR) project identified bridges of similar size and design (predominantly single-span bridges or culverts), which allowed the opportunity for similar designs and economies of scale, optimizing the ability to complete the design and construction of individual bridges more quickly. PennDOT estimates that replacing the structures using conventional contract procedures would have taken eight to 12 years, whereas a P3 project compressed the schedule to approximately five years.
At $1.2 billion over a 28-year term (including 25 years of maintenance), it is the largest multi-asset, multi-location P3 project of its kind in the United States.
Pennsylvania is among the nation’s leaders in terms of state and locally-owned bridges (approximately 32,000) and total lane miles maintained (just over 250,000). Because the RBR project was a multi-location project, it had to accommodate some of the most diverse geography of any state (mountains, valleys, rivers/streams, Karstic conditions, etc.). Additionally, Pennsylvania’s governmental structure and PennDOT’s organization required the successful Development Entity (DE) to coordinate with 67 counties that collectively formed 11 PennDOT Engineering Districts, each with respective preferences regarding transportation infrastructure.
McCormick Taylor served as both a technical advisor to the PennDOT P3 Office in all communications and outreach measures, as well as in the role of Public Involvement Management Consultant to PennDOT’s management team on the RBR project.




HOW WE HELPED
During the RBR project’s first year, the public involvement (PI) process was not being fully conducted in accordance with PennDOT’s guidelines. For example, a municipality could indicate that they did not want a public meeting or preferred to wait until closer to construction to hold one, which did not provide the public with the opportunity to comment during the NEPA process for each respective bridge.
As a result, a revised PI approach was developed in conjunction with PennDOT and FHWA, which included adding McCormick Taylor to PennDOT’s management team as the Public Involvement Management Consultant. Additional details of the revised PI approach included:
- Required public meeting or plans display during NEPA process for all projects.
- Reviewed all projects to make sure they were compliant with the PI approach
- Resolved any past issues with PI
McCormick Taylor was responsible for ensuring all the requirements were being met by the private partner Development Entity (DE). The most significant portion of this regarded the public meetings and plans displayed that were required to be held and made available for each bridge prior to construction start. McCormick Taylor organized, coordinated, attended and audited every public meeting, and also served as quality assurance on every required press release related to each RBR bridge (over 1,000 press releases).
McCormick Taylor served on the RBR project team for internal communications and outreach as well. As the project approached the final years of Design and Construction, McCormick Taylor supported PennDOT in preparation to transition to the Maintenance phase of the project; a 25-year period where the DE takes over maintenance responsibilities for all 558 bridges. McCormick Taylor organized, developed all materials and content, and moderated a series of annual webinars specific to internal communications and education regarding the transition to the Maintenance phase. This included the development of the RBR Maintenance Guidance Document (Pub. 104).
Additionally, our GIS team developed the Rapid Bridge Replacement Project Map, an intuitive and highly visual GIS web application that connects the public with detailed, real-time information about bridge construction in communities across the state.
RESULTS
In the final year of the Design and Construction phase, McCormick Taylor supported PennDOT as they gathered lessons learned data through a series of workshops and interviews with over 140 representatives from PennDOT’s 11 Engineering Districts; executive management team and P3 Office; subject matter experts; and consultant support staff. This data was ultimately compiled, analyzed and distributed in 2019 as the PennDOT Rapid Bridge Replacement Project Lessons Learned Report.
As of August 2020, all 558 bridges have been replaced and are open to traffic. The Commonwealth retains ownership of the bridges, but the Development Entity is responsible for maintaining the bridges until the end of 2042.
